DIEGO GARCIA
Seumur hidupku memang tak pernah mendengar nama ini. Tiba-tiba nama Deigo Carcia muncul dalam kehangatan Tragedi MH370
Russia “Puzzled” Over Malaysia
Walaupun aku kurang berminat dengan mana-mana andaian atau teori timur dan barat, aku tak berminat juga untuk memberi sebarang ulasan. Aku cuma tertarik untuk mengetahui kat mana menatang Diego Garcia ni.

Seumur hidupku memang tak pernah mendengar nama ini. Tiba-tiba nama Deigo Carcia muncul dalam kehangatan Tragedi MH370
Setelah beberapa hari tragedi kehilangan MH370 pada 080121H Mac di 120 batu nautika ke Timur Kota Bharu, pelbagai teori dari pelbagai pihak di serata dunia yang membuat andaian mengikut apa yang mereka rasakan betu,
Sehingga 13 Mac, tiada sebarang tanda ditemui di Laut China Selatan (LCS). Pada 14 Mac terdapat andaian dan pertanda menyatakan pesawat bertukar arah ke Lautan Hindi atau Selat Melaka. Operasi pencarian di LCS ditamatkan dan tumpuan diubah ke utara Lautan Hindi (utara Selat Melaka dan Laut Andaman).
Pada 20 Mac, PM Australia mengumumkan bahawa satelit negaranya dapat menegsan objek di selatan Lautan Hindi kira-kira 2500 km dari pantai Perth. Operasi pencarian diubah ke selatan Lautan Hindi.
Pada 22 Mac 14, PM Malaysia, DS Najib mengumumkan bahawa berdasarkan jajaran maklumat dari satelit IMARSAT dan AAIB (UK), penerbangan pesawat MH370 berakhir di selatan lautan Hindi. Maka operasi pencarian ditumpukan sepenuhnya di kawasan tersebut.
Dari awal kehilangan MH370 berpuluh-puluh teori diterbitkan dalam pelbagai saluran media. Antaranya:
http://www.whatdoesitmean.com/index1753.htm
March 14, 2014
By: Sorcha Faal, and as reported to her Western Subscribers
    |
A new report circulating in the Kremlin today prepared by the Main Intelligence Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces (GRU) states that Aerospace Defence Forces (VKO) experts remain “puzzled” as to why the United States Navy captured and then diverted a Malaysia Airlines civilian aircraft from its intended flight-path to their vast and highly-secretive Indian Ocean base located on the Diego Garcia atoll.
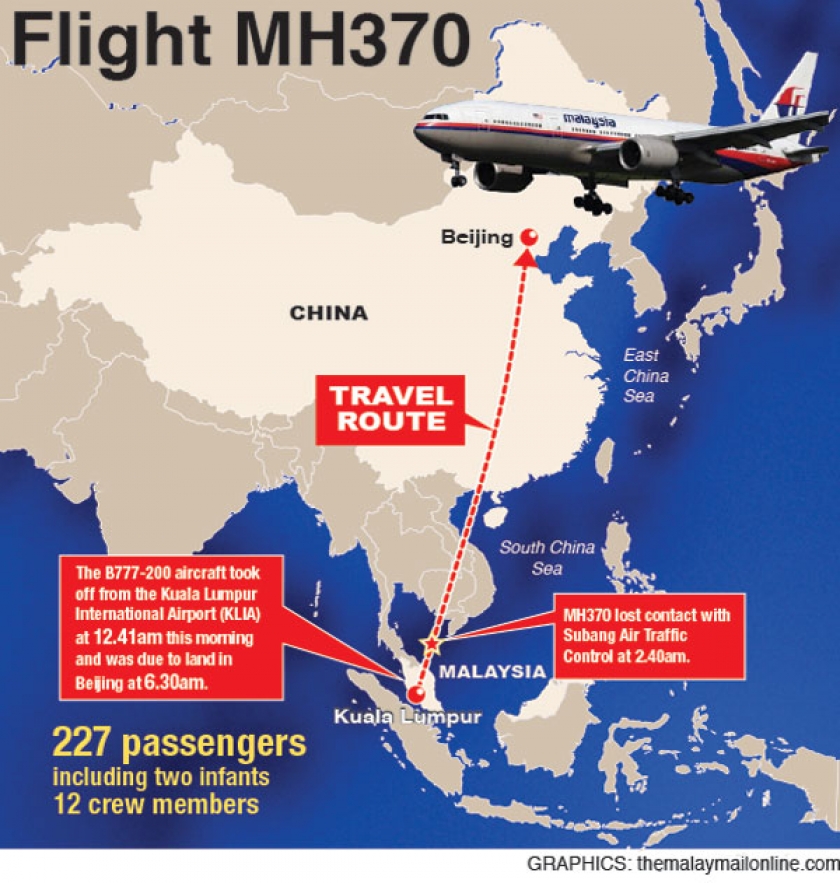
According to this report, MAS Flight MH370 (also marketed as China Southern Airlines Flight 748 through a codeshare) was a scheduled passenger flight from Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, to Beijing, China, when on 8 March this Boeing 777-200ER aircraft“disappeared” in flight with 227 passengers on board from 15 countries, most of whom were Chinese, and 12 crew members.
Interesting to note, this report says, was that Flight 370 was already under GRU “surveillance” after it received a “highly suspicious” cargo load that had been traced to the Indian Ocean nation Republic of Seychelles , and where it had previously been aboard the US-flagged container ship MV Maersk Alabama.
What first aroused GRU suspicions regarding the MV Maersk Alabama, this report continues, was that within 24-hours of off-loading this “highly suspicious” cargo load bound for Malaysia Airlines Flight 370, the two highly-trained US Navy Seals assigned to protect it, Mark Daniel Kennedy, 43, and Jeffrey Keith Reynolds, 44, were found dead under “suspicious circumstances.”
Both Kennedy and Reynolds, this report says, were employed by the Virginia Beach, Virginia-based maritime security firm The Trident Group which was founded by US Naval Special Ops Personnel (SEAL’s) and Senior US Naval Surface Warfare Officers and has long been known by the GRU to protect vital transfers of both atomic and biological materials throughout the world.
Upon GRU “assests” confirming that this “highly suspicious” cargo was aboard MH370 on 8 March, this report notes, Moscow notified China
However, this report says, and as yet for still unknown reasons, the MSS was preparing to divert Flight 370 from its scheduled destination of Beijing to Haikou Meilan International Airport (MAK) located in Hainan Province (aka Hainan Island
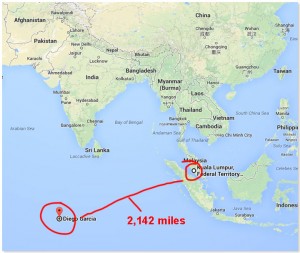
Prior to entering the People Liberation Army (PLA) protected zones of the South China Sea known as the Spratly Islands, this report continues, Flight 370 “significantly deviated” from its flight course and was tracked by VKO satellites and radar flying into the Indian Ocean region and completing its nearly 3,447 kilometer (2,142 miles) flight to Diego Garcia.
Critical to note about Flight 370’s flight deviation, GRU experts in this report say, was that it occurred during the same time period that all of the Spratly Island mobile-phone comm
China Mobile, it should be noted, extended telephone coverage in the Spratly Islands in 2011 so that PLA soldiers stationed on the islands, fishermen, and merchant vessels within the area would be able to use mobile services, and can also provide assistance during storms and sea rescues.
As to how the US Navy was able to divert Flight 370 to its Diego Garcia base, this report says, appears to have been accomplished remotely as this Boeing 777-200ER aircraft is equipped with a fly-by-wire (FBW) system that replaces the conventional manual flight controls of an aircraft with an electronic interface allowing it to be controlled like any drone-type aircraft.
However, this report notes, though this aircraft can be controlled remotely, the same cannot be said of itscomm systems which can only be shut down manually; and in the case of Flight 370, its data reporting system was shut down at 1.07 am, followed by its transponder (which transmits location and altitude) which was shut down at 1.21 am.
What remains “perplexing” about this incident, GRU analysts in this report say, are why the American mainstream media outlets have yet to demand from the Obama regime the radar plots and satellite images of the Indian Ocean and South China Sea regions as the US military covers this entire area from Diego Garcia like no other seas in the world due to its vital shipping and air lanes.
Most sadly, this report concludes, the US is actually able to conceal the reason(s) for the “disappearance” of Flight 370 as they have already done so after the events of 11 September 2001 when the then Bush regime “disappeared” American Airlnes Flight 77 and its 64 passengers and crew after falsely claiming it hit the Pentagon, but which was confirmed by the CNN News Service not to have happened.
Walaupun aku kurang berminat dengan mana-mana andaian atau teori timur dan barat, aku tak berminat juga untuk memberi sebarang ulasan. Aku cuma tertarik untuk mengetahui kat mana menatang Diego Garcia ni.
DIEGO GARCIA

Diego Garcia is a tropical, footprint-shaped coral atoll located south of the equator in the central Indian Ocean. It is part of the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT).
The atoll is approximately 1,970 nautical miles (3,650 km) east of the coast of African east coastline (at Tanzania), 967 nautical miles (1,790 km) south-southwest of the southern tip of India (at Kanyakumari) and 2,550 nautical miles (4,720 km) west-northwest of the west coast of Australia (at Cape Range National park, Perth). Diego Garcia lies in the Chagos Archipelago at the southernmost tip of the Chagos-Laccadive Ridge, a vast submarine range in the Indian Ocean, topped by a long chain of coral reefs, atolls, and islands comprising Lakshadweep, Maldives, and the Chagos Archipelago. Local time is UTC + 06.00 year-around.


Pre-history
According to Southern Maldivian oral tradition, traders and fishermen were occasionally lost at sea and got stranded in one of the islands of the Chagos. Eventually they were rescued and brought back home. However, the different atolls of the Chagos have no individual names in the Maldivian oral traditions. The island may have been visited during the Austronesian diaspora around 700 AD, and some] say the old Maldivian name for the islands originated from Malagasy. It is also suggested that the Arabs, who reached Lakshaweep and Maldives around 900 AD, may have visited the Chagos, and that Zheng He may have sailed close in 1413-1415, since it is documented on a Ming Dynasty map.
European Discovery
The uninhabited islands were discovered by the Portuguese navigator, explorer and diplomat Pedro Mascarenhas in 1512, first named as Dom Garcia, in honor of his patron, Dom Garcia de Noronha during his voyage of 1512–1513, but there is little corroborative evidence for this. Another Portuguese expedition with Spanish sailor Diego Garcia de Moquer rediscovered the island in 1544 and named it after himself. The misnomer "Diego" could have been made unwillingly by the British ever since, as they copied the Portuguese maps. It is assumed that the island was named after one of its discoverers, or that two captains arrived on the island in quick succession - the one by the name of Garcia, the other with name Diego. Also, a cacography of the saying Deo Gracias ("Thank God") is eligible for the attribution of the atoll.
Tradition suggests that the island took its name from the Spanish navigator Diego García de Moguer, who discovered the island in the 1500s. Garcia was the explorer who sailed to the Rio de la Plata in 1526, and possibly with Hernando de Soto’s voyage. García headed a Portuguese expedition in the Indian ocean in 1554 and died before completing the return travel. Portuguese scholars believe that Garcia's supposed Christian name, "Diego", was a misnomer or a misreading from Deo Gracias, that came into use towards the end of the 16th century and turned the name into Diego Garcia. Although the Cantino planisphere (1504) and the Ruysch map (1507) clearly delineate the Maldive Islands, giving them the same names, they do not show any islands to the south which can be identified as the Chagos archipelago.
The Sebastian Cabot map (Antwerp 1544) shows a number of islands to the south which may be the Mascarene Islands. The first map which identifies and names "Los Chagos" (in about the right position) is that of Pierre Desceliers (Dieppe 1550), although Diego Garcia is not named. An island called "Don Garcia" appears on the Theatrum Orbis Terrarum of Abraham Ortelius (Antwerp 1570), together with "Dos Compagnos", slightly to the north. It may be the case that "Don Garcia" was named after Garcia de Noronha, although there no evidence exists to support this supposition. The island is also shown as 'Don Garcia' on Mercator’s Nova et Aucta Orbis Terrae Descriptio ad Usum Navigatium Emendate (Duisburg 1569). However, on the Vera Totius Expeditionis Nauticae Description of Jodocus Hondius (London 1589), "Don Garcia" mysteriously changes its name to "I. de Dio Gratia", while the "I. de Chagues" appears close by.
The first map to delineate the island under its present name, Diego Garcia, is the World Map of Edward Wright (London 1599), possibly as a result of misreading Dio (or simply "D.") as Diego, and Gratia as Garcia. The Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Geographica of Henricus Hondius (Antwerp 1630) repeats Wright's misreading of the name, which is then proliferated on all subsequent Dutch maps of the period, and to the present day.


Settlement of the island
Diego Garcia and the rest of the Chagos islands were uninhabited until the late 18th century. In 1778 the French Governor of Mauritius granted Monsieur Dupuit de la Faye the island of Diego Garcia, and there is evidence of temporary French visits to collect coconuts and fish. Several Frenchmen living in "a dozen huts" abandoned Diego Garcia when the British East India Company attempted to establish a settlement there in April 1786. The supplies of the 275 settlers were overwhelmed by 250 survivors of the wreck of the British East Indian Ship ATLAS in May, and the colony failed in October. Following the departure of the British, the French colony of Mauritius began marooning lepers on Diego Garcia, and in 1793 the French established a coconut plantation using slave labour, which also exported cordage made from coconut fiber, and sea cucumbers, known as a delicacy in the orient.
Diego Garcia became a colony of the UK after the Napoleonic Wars as part of the Traety of Paris (1814), and from 1814 to 1965 it was administered from Mauritius. On Diego Garcia, the main plantations were located at East Point, the main settlement on the eastern rim of the atoll; Minni Minni, 4.5 kilometres (2.8 mi) north of East Point; and Pointe Marianne, on the western rim, all located on the lagoon side of the atoll rim. The workers lived at these locations, and at villages scattered around the island.
From 1881 until 1888 Diego Garcia was the location of two coaling stations for steamships crossing the Indian Ocean.
In 1882 the French-financed, Mauritian-based Societe Huilere de Diego et Peros (the "Oilmaking Company of Diego and Peros"), consolidated all the plantations in the Chagos under its control.


The US Navy operates Naval Support Facility (NSF) Diego Garcia, a large naval ship and submarine support base, military air base, communications and space-tracking facility, and an anchorage for pre-positioned military supplies for regional operations aboard Military Sealift Command ships in the lagoon. Mauritius sought to regain sovereignty, sold to the UK in 1965, over the Chagos Archipelago. Between 1968 and 1973, the Chagossians, then numbering about 2,000 people, were resettled by the British government to Mauritius and Seychelles to allow ths US to establish a military base on the island. Today, the exiled Chagossians are still trying to return, claiming that the forced expulsion was illegal.


20th Century
In 1914 the island was visited by the German light cruiser SMS Emden half-way through its historic commerce raiding cruise during the first months of World War I. In 1942 the British established RAF Station Diego Garcia as an advanced flying boat unit at the East Point Plantation, staffed and equipped from No 205 and No 240 Squadrons, then stationed on Ceylon. Both Catalina and Sunderland aircraft were flown during the course of World War II in search of Japanese and German submarines and surface raiders. Following the conclusion of hostilities, the station was closed on 30 April 1946.
In 1962 the Chagos Agalega Company of the British colony of Seychelles purchased the Societe Huiliere de Diego et Peros and moved company headquarters to Seychelles.
In the early 1960s, the UK was withdrawing its military presence from the Indian Ocean area, not including the base at RAF Gan to the north of Diego Garcia in the Maldives (which remained open until 1976), and agreed to permit the United States to establish a Naval Communication Station on one of its island territories there. The United States requested an unpopulated island belonging to the UK to avoid political difficulties with newly independent countries, and ultimately the UK and United States agreed that Diego Garcia was a suitable location.
Purchase by the United Kingdom
To accomplish the UK/United States mutual defense strategy, in November 1965, the UK purchased the Chagos Archipelago, which includes Diego Garcia, from the then self-governing colony of Mauritius for £3 million to create the (BIOT, with the intent of ultimately closing the plantations to provide the uninhabited British territory from which the United States would conduct its military activities in the region. In April 1966 the British Government bought the entire assets of the Chagos Agalega Company in the BIOT for £600,000 and administered them as a government enterprise while awaiting United States funding of the proposed facilities, with an interim objective of paying for the administrative expenses of the new territory. However, the plantations, both under their previous private ownership and under government administration, proved consistently unprofitable due to the introduction of new oils and lubricants in the international marketplace, and the establishment of vast coconut plantations in the East Indies and the Philippines.
On 30 December 1966, the United States and the UK executed an agreement through an Exchange of Notes which permits the United States to use the BIOT for defense purposes for 50 years (through December 2016), followed by a 20-year optional extension (to 2036) to which both parties must agree by December 2014. No monetary payment was made from the United States to the UK as part of this agreement or any subsequent amendment. Rather, the United Kingdom received a USD14 million discount from the United States on the acquisition of submarine-launched ballistic missile system Polaris missiles per a now-declassified addendum to the 1966 agreement.
Arrival of the United States Navy
In March 1971, United States Naval construction battalions (Seebees) arrived on Diego Garcia to begin the construction of the Communications Station and an airfield. To satisfy the terms of an agreement between the UK and the United States for an uninhabited island, the plantation on Diego Garcia was closed in October of that year. The plantation workers and their families were relocated to the plantations on Peros Bahnos and Salomon atolls to the northwest; those who requested were transported to the Seychelles or Mauritius. In 1972, the UK decided to close the plantations throughout the Chagos, including those on Peros Banhos and the Salomon Islands, and deported the Ilois to their ancestral homes on either the Seychelles or Mauritius. The then-independent Mauritian government refused to accept the islanders without payment, and in 1974, the UK gave the Mauritian government an additional ₤650,000 to resettle the islanders.
By 1973, construction of the Naval Communications Station (NAVCOMMSTA) was completed. In the early 1970s, setbacks to United States military capabilities in the region including the Fall of Saigon, victory of the Khmer Rouge in Cambodia , the closure of the Peshawar Air Station listening post in Pakistan and Kagnew Station in Ethiopia, the Mayaquez incident, and the build-up of Soviet Naval presence in Aden and a Soviet airbase at Berbera, Somalia, caused the United States to request, and the UK to approve, permission to build a fleet anchorage and enlarged airfield on Diego Garcia, and the Seabees doubled the number of workers constructing these facilities.
Following the fall of the Shah of Iran and the Iran Hostage Crisis in 1979–1980, the West became concerned with ensuring the flow of oil from the Persian Gulf through the Straits of Hormuz, and the United States received permission for a $400 million expansion of the military facilities on Diego Garcia consisting of two parallel 12,000-foot-long (3,700 m) runways, expansive parking aprons for heavy bombers, 20 new anchorages in the lagoon, a deep water pier, port facilities for the largest naval vessels in the American or British fleet, aircraft hangars, maintenance buildings and an air terminal, a 1,340,000 barrels (213,000 m3) fuel storage area, and billeting and messing facilities for thousands of sailors and support personnel.
Naval Support Facility Established
On 1 October 1977, Naval Support Facility, Diego Garcia, was established as the senior United States Navy command on the island. At the time the NAVCOMMSTA was the primary tenant, but as the new major facilities were completed, most notably the expanded anchorage and mooring area and the extended airfield, other tenants were commissioned.
In 1980, the USN established the Near-Term Prepositioned Force (NTPF of 16 ships. Then NTPF became the Afloat Prepositioning Force (AFP) and eventually Maritime Prepositioning Ship Squadron Two (MPSRON 2) consisting of 20 deep-water pre-positioned logistics ships anchored in the lagoon.
In 1981, the Naval Air Facility NSF) was commissioned. It was decommissioned in 1987 and its responsibilities returned to the NSF.
In 1982, Construction activities were transferred from the Seabees to a consortium of civilian contractors, and the majority of the projects were completed by 1988. On 26 March 1982, Barbara Shuping and five other women were assigned to the NSF. Prior to this assignment, no women had lived on the island since those on the plantation in 1971.
In 1985, the new port facilities were completed, and the USS Saratoga (CV-60) was the first aircraft carrier to tie up.
Strategic Air Command began deploying Boeing B-52 Stratofortress bombers and aerial refuelling aircraft to the newly completed airfield facilities in 1987. Following the Iraqi Invasion of Kuwait in August 1990, three ships of COMPSRON 2 sorties, delivering a Marine Expeditionary Brigade to Saudi Arabia for participation in the Gulf War. Other COMPSRON 2 ships offloaded the munitions, bombs, and fuel on Diego Garcia that were required for the American bomber fleet that deployed to airfield. Subsequently, B-52G bombers flew more than 200 17-hour bombing missions over 44 days and dropped more than 800,000 short tons (730,000,000 kg) of bombs on Iraqi forces in Iraq and Kuwait. One of the B-52s crashed from mechanical failures just north of the island with the loss of three of its six-man crew. Beginning on 7 October 2001, the United States again commenced military operations from Diego Garcia using B-1, B-2, and B-52 bombers to attack enemy targets in Afghanistan following the attacks on New York City and the Pentagon. A B-1 bomber was lost on 12 December 2001 to mechanical failures just after take off from the island, but the crew survived and was rescued by the USS Russell (DDG-59). Combat operations resumed in the spring of 2003, with MPSRON TWO sortieing to the Persian Gulf for Operation Iraqi Freedom, and bombing operations began again, this time against Iraq. Bomber operations ceased from Diego Garcia on 15 August 2006.
.
.
Protection from Industry
In 2004, the UK applied for, and received, Ramsar Site wetlands conservation status for the lagoon and other waters of Diego Garcia.
On 1 April 2010, the UK Cabinet declared the Chagos Archipelago a Marine Protected Area (MPA) and prohibited all extractive industry, including fishing and oil and gas exploration. It is unclear whether Diego Garcia is included in the MPA.
Inhabitants
Diego Garcia had no permanent inhabitants when discovered by the Spanish explorer Diego Garcia de Moquer in the 16th century and remained so until settled as a French colony in 1793.
French Settlement
Most inhabitants of Diego Garcia through the period from 1793 to 1971 were plantation workers, but also included Franco-Mauritian managers, Indo-Mauritian administrators, Mauritian and Seychellois contract employees, and in the late 19th Century, Chinese and Somali employees.
A distinct Creole culture called the Ilois, which means "Islanders" in French Creole, evolved from these workers. The Ilois, now called Chagos Islanders or Chagossians since the late 1990s, were descended primarily from slaves brought to the island from Madagarcar by the French between 1793 and 1810, and Malay slaves from the slave market on Pulo Nyas, an island off the northwest coast of Sumatra, from around 1820 until the slave trade ended following the Slavery Abolition Act of 1833. The Ilois also evolved a French-based Creole dialect now called Chagossian Creole.
Throughout their recorded history, the plantations of the Chagos Archipelago had a population of approximately 1,000 individuals, about two-thirds of whom lived on Diego Garcia. A peak population of 1,142 on all islands was recorded in 1953.
The primary industry throughout the island's colonial period consisted of coconut plantations producing copra and/or coconut oil until closure of the plantations and relocation of the inhabitants in October 1971. For a brief period in the 1880s it served as a coaling station for steamships transiting the Indian Ocean from the Suez Canal to Australia.
Deportation of 1971
All the inhabitants of Diego Garcia were relocated to other islands in the Chagos Archipelago or to Mauritius or Seychelles by 1971 to satisfy the requirements of a UK/United States Exchange of Notes signed in 1966 to depopulate the island when the United States constructed a base upon it. No current agreement exists on how many of the evacuees met the criteria to be an Ilois, and thus be an indigenous person at the time of their removal, but the UK and Mauritian governments agreed in 1972 that 426 families, numbering 1,151 individuals were due compensation payments as exiled Ilois. The total number of people certified as Ilois by the Mauritian Government's Ilois Trust Fund Board in 1982 was 1,579. This relocation decision remains in litigation as of 2010.
After 1971
Between 1971 and 2001, the only residents on Diego Garcia were UK and United States military personnel and civilian employees of those countries. These included contract employees from the Phillipines and Mauritius, including some Ilois. During the combat operations from the atoll against Afghanistan (2001–2006) and Iraq (2003–2006), a number of allied militaries were based on the island including Australian, Japanese and the Republic of Korea. According to David Vine, "Today, at any given time, 3,000 to 5,000 U.S. troops and civilian support staff live on the island. The inhabitants today do not rely on the island and the surrounding waters for sustenance. Although some recreational fishing for consumption is permitted, all other food is shipped in by sea or air.
Politics
Diego Garcia is the largest and only inhabited island in the BIOT and Overseas Territory of the UK, and, usually abbreviated as "BIOT". The Government of BIOT consists of Commissioner appointed by the Queen. The Commissioner is assisted by an Administrator and small staff, and is based in London and resident in the Foreign and Commonwealth Office.
Originally colonized by the French, Diego Garcia was ceded, along with the rest of the Chagos Archipelago, to the United Kingdom in the Treaty of Paris (1814) at the conclusion of a portion of the Napoleonic Wars. Diego Garcia and the Chagos Archipelago were administered by the colonial government on the island of Mauritius until 1965, when the UK purchased them from the self-governing government of Mauritius for £3 million, and declared them to be a separate British Overseas Territory. The BIOT administration was moved to Seychelles following the independence of Mauritius in 1968 until the independence of Seychelles in 1976, and to a desk in the Foreign and Commonwealth Office in London since.


Military Administration
UK represents the Territory internationally. A local government as normally envisioned does not exist. Rather, the administration is represented in the Territory by the Officer commanding British Forces on Diego Garcia, the "Brit Rep". Laws and regulations are promulgated by the Commissioner and enforced in the BIOT by British Rep.
Of major concern to the BIOT administration is the relationship with the United States military forces resident on Diego Garcia. An annual meeting called "The Pol-Mil Talks" (for Political-Military) of all concerned is held at the Foreign and Commonwealth Office in London to resolve pertinent issues. These resolutions are formalized by an "Exchange of Notes", or, since 2001, an "Exchange of Letters".
Transnational Political Issues
There are two transnational political issues which affect Diego Garcia and the BIOT, through the British government. As these issues affect the BIOT as a whole, not just the island of Diego Garcia, they are more appropriately and completely addressed in the Wikipedia articles BIOT and Depopulation of Diego Garcia.
First, the island nation of Mauritius claims the Chagos Archipelago (which is coterminous with the BIOT), including Diego Garcia. A subsidiary issue is the Mauritian opposition to the UK Government's declaration of 1 April 2010 that the BIOT is a Marine Protected Area with fishing and extractive industry (including oil and gas exploration) prohibited.
Second, the issue of compensation and repatriation of the former inhabitants, exiled since 1973, continues in litigation and as of August 2010 had been submitted to the European Court of Human Rights by a group of former residents. Some] groups allege that Diego Garcia and its territorial waters out to 3 nautical miles (6 km) have been restricted from public access without permission of the BIOT Government since 1971.
Prison Site Allegations
In June 2004, the British Foreign Secretary Jack Straw stated that United States authorities had repeatedly assured him that no detainees had passed in transit through Diego Garcia or were disembarked there. In October 2007 the all-party Foreign Affairs Committee of the British Parliament announced that it would launch an investigation of continued allegations of a prison camp on Diego Garcia, which it claimed were twice confirmed by comments made by Retired United States Army General Barry McCaffrey. On July 31, 2008, an unnamed former White House official alleged that the United States had imprisoned and interrogated at least one suspect on Diego Garcia during 2002 and possibly 2003.
Manfred Nowak, one of five of the UN Special Rapporteur on torture,says that credible evidence exists supporting allegations that ships serving as black sites have used Diego Garcia as a base. The human rights group Reprieve alleges that United States-operated ships moored outside the territorial waters of Diego Garcia were used to incarcerate and torture detainees.
Rendition Flight Refuelling Admission
Diego Garcia is rumoured to have been one of the locations of the CIA black sites. Several groups claim that the military base on Diego Garcia has been used by the United States government for transport of prisoners involved in the controversial extra-ordinary rendition program, an allegation formally reported to the Council of Europe in June 2007. On February 21, 2008, British Foreign Secretary David Miliband admitted that two United States extraordinary rendition flights refuelled on Diego Garcia in 2002. No reference was made to whether prisoners were on board the aircraft at the time. Khalid Sheikh Mohammed is one of the ‘high value detainees’ suspected to have been held in Diego Garcia.
WikiLeaks CableGate Disclosures (2010)
According to Wikileaks CableGate documents (reference ID "09LONDON1156"), in a calculated move planned in 2009, the UK proposed that the BIOT become a "marine reserve" with the aim of preventing the former inhabitants from returning to their lands. A summary of the diplomatic cable is as follows: HMG would like to establish a "marine park" or "reserve" providing comprehensive environmental protection to the reefs and waters of the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT), a senior Foreign and Commonwealth Office (FCO) official informed Polcouns on May 12. The official insisted that the establishment of a marine park—the world's largest—would in no way impinge on USG use of the BIOT, including Diego Garcia, for military purposes. He agreed that the UK and United States should carefully negotiate the details of the marine reserve to assure that United States interests were safeguarded and the strategic value of BIOT was upheld. He said that the BIOT's former inhabitants would find it difficult, if not impossible, to pursue their claim for resettlement on the islands if the entire Chagos Archipelago were a marine reserve.
Additionally, Diego Garcia was used as a storage section for U.S. cluster bombs as a way of avoiding UK parliamentary oversight.
Geography
Diego Garcia is the largest land mass in the Chagos Archipelago (which includes Peros Banhos, the Solomon Islands, the Three Brothers, the Eqmont Islands and the Great Chagos Bank), being an atoll occupying approximately 174 square kilometres (67 sq mi), of which 27.19 square kilometres (10 sq mi) is dry land. The continuous portion of the atoll rim stretches 40 miles (64 km) from one end to the other, enclosing a lagoon 13 miles (21 km) long and up to 7 miles (11 km) wide, with a 4-mile (6 km) pass opening at the north. There are three small islands located in the pass.
The island consists of the largest continuous atolls in the world. The dryland rim varies in width from a few hundred metres to 2.4 km. Typical of coral atolls, it has a maximum elevation on some dunes on the ocean side of the rim of nine metres (30 ft) above mean low water. The rim nearly encloses a lagoon about 19 kilometres (12 mi) long and up to 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) wide. The atoll forms a nearly complete rim of land around a lagoon, enclosing 90 percent of its perimeter, with an opening only in the north. The main island is the largest of about 60 islands which form the Chagos Archipelago. Besides the main island, there are three small islets at the mouth of the lagoon: West Island (3.4 ha/8.4 acres); Middle Island (6 ha/14.8 acres); and East Island (11.75 ha/29 acres). A fourth island shown on some] maps, Anniversary Island one km (1,100 yards) southwest of Middle Island, appears as just a sand bar on satellite images. Both Middle Island and Anniversary Island are part of the Spur Reef complex.
The total area of the atoll is approximately 170 square kilometres (65.6 sq mi). The lagoon area is approximately 120 square kilometres (46.3 sq mi) with depths ranging down to about 25 m (80 feet). The total land area (excluding peripheral reefs) is approximately 30 square kilometres (12 sq mi). The coral reef surrounding the seaward side of the atoll is generally broad, flat, and shallow at about 1 m (3 feet) below mean sea level in most locations and varying from 100 to 200 m (300 to 650 feet) in width. This fringing seaward reef shelf comprises an area of approximately 35.2 square kilometres (14 sq mi). At the outer edge of the reef shelf, the bottom slopes very steeply into deep water, at some locations dropping to more than 450 metres (1,500 ft) within 1 km (0.6 miles) of the shore.
In the lagoon, numerous coral heads present hazards to navigation. The shallow reef shelf surrounding the island on the ocean side offers no ocean-side anchorage. The channel and anchorage areas in the northern half of the lagoon are dredged, along with the pre-1971 ship turning basin. Significant salt-water wetlands called barachois exist in the southern half of the lagoon. These are small lagoons off of the main lagoon, filled with seawater at high tide and dry at low tide. Scientific expeditions in 1996 and 2006 described the lagoon and surrounding waters of Diego Garcia, along with the rest of the Chagos Archipelago, as "exceptionally unpolluted" and "pristine".
There are no endemic species of plants, birds, amphibians, reptiles, mollusks, crustaceans, or mammals on Diego Garcia or in the surrounding waters. There are several endemic fish and aquatic invertebrates. All plants, wildlife, and aquatic species are protected to one degree or another. In addition, much of the lagoon waters are protected wetlands as a designated Ramsar Site, and large parts of the island are nature preserves. Diego Garcia is frequently subject to earthquakes caused by tectonic plate movement along the Carlsberg Ridge located just to the west of the island. One was recorded in 1812; one measuring 7.6 on the Richter Scale hit on November 30, 1983, at 21:46 local time and lasted 142 seconds, resulting in a small tsunami which raised wave height in the lagoon to 1.5 metres (5 ft), and another on December 2, 2002, an earthquake measuring 4.6 on the Richter Scale struck the island at 12:21 a.m.
In December 2004, a tsunami generated near Indonesia caused minor shoreline erosion on Barton Point (the northeast point of the atoll of Diego Garcia).
Oceanography
Diego Garcia lies within the influence of the South Equatorial current year-round. The surface currents of the Indian Ocean also have a monsoonal regime associated with the Asian Monsoonal wind regime. Sea surface temperatures are in the range of 80-84 °F/26-28 °C year-round.

.



Fresh Water Supply
Diego Garcia is the above-water rim of a coral atoll composed of Holocene coral rubble and sand to the depth of about 36 metres (120 ft), overlaying Pleistocene limestone deposited at the then-sea level on top of a seamount rising approximately 1,800 metres (6,000 ft) from the floor of the Indian Ocean. The Holocene sediments are porous and completely saturated with sea water. Any rain falling on the above-water rim quickly percolates through the surface sand and encounters the salt water underneath. Diego Garcia is of sufficient width to minimise tidal fluctuations in the aquifer, and the rainfall (in excess of 102.5 inches/260 cm per year on average) is sufficient in amount and periodicity for the fresh water to form a series of convex, fresh-water, Ghyben-Herzberg lenses, floating on the heavier salt water in the saturated sediments.
The horizontal structure of each lens is influenced by variations in the type and porosity of the sub-surface deposits, which on Diego Garcia are minor. At depth, the lens is globular; near the surface it generally conforms to the shape of the island. When a Ghyben-Herzberg lens is fully formed, its floating nature will push a freshwater above mean sea level, and if the island is wide enough, the depth of the lens below mean sea level will be 40 times the height of the water table above sea level. On Diego Garcia this equates to a maximum depth of 20 metres. However, the actual size and depth of each lens is dependent on the width and shape of the island at that point, the permeability of the aquifer, and the equilibrium between recharging rainfall and losses to evaporation to the atmosphere, transpiration by plants, tidal advection, and human use.
In the plantation period, shallow wells, supplemented by rainwater collected in cisterns, provided sufficient water for the pastoral life style of the small population. On Diego Garcia today, the military base uses over 100 shallow "horizontal" wells to produce over 560,000 liters per day from the "Cantonment" lens on the northwest arm of the island - sufficient water for western-style usage for a population of 3,500. It is estimated that this 3.7 Ssq km lens holds 19 million cubic m of fresh water and has an average daily recharge from rainfall of over 10,000 cubic m, of which 40% remains in the lens and 60% is lost through evapotranspiration.
Extracting fresh water from a lens for human consumption requires careful calculation of the sustainable yield of the lens by season because each lens is susceptible to corruption by salt-water intrusion caused by overuse or drought. In addition, overwash by tsunamis and tropical storms has corrupted lenses in the Maldives and several Pacific islands. Vertical wells can cause salt upconing into the lens, and over-extraction will reduce fresh water pressure resulting in lateral intrusion by seawater. Because the porosity of the surface soil results in virtually zero runoff, lenses are easily polluted by fecal waste, burials, and chemical spills. Corruption of a lens can take years to "flush out" and reform, depending on the ratio of recharge to losses.
There are a few natural depressions on the atoll rim that capture the abundant rainfall to form areas of fresh-water wetlands. Two are of significance to island wildlife and to recharge their respective fresh-water lenses. One of these is centered on the northwest point of the atoll, another is found near the Point Marianne Cemetery on the southeast end of the airfield. Other, smaller freshwater wetlands are found along the east side of the runway, and in the vicinity of the receiver antenna field on the northwest arm of the atoll.
Climate data for Diego Garcia
Month
|
Jan
|
Feb
|
Mar
|
Apr
|
May
|
Jun
|
Jul
|
Aug
|
Sep
|
Oct
|
Nov
|
Dec
|
Year
|
Record high °C (°F)
|
32
(90) |
32
(90) |
33
(91) |
33
(91) |
33
(91) |
33
(91) |
32
(90) |
32
(90) |
32
(90) |
33
(91) |
33
(91) |
32
(90) |
33
(91) |
Average high °C (°F)
|
31
(88) |
31
(88) |
30
(86) |
30
(86) |
30
(86) |
30
(86) |
30
(86) |
30
(86) |
30
(86) |
30
(86) |
30
(86) |
31
(88) |
30.3
(86.5) |
Average low °C (°F)
|
28
(82) |
28
(82) |
28
(82) |
28
(82) |
27
(81) |
27
(81) |
27
(81) |
27
(81) |
28
(82) |
28
(82) |
28
(82) |
28
(82) |
27.7
(81.7) |
Record low °C (°F)
|
26
(79) |
25
(77) |
25
(77) |
26
(79) |
26
(79) |
25
(77) |
26
(79) |
25
(77) |
25
(77) |
26
(79) |
26
(79) |
25
(77) |
25
(77) |
Precipitation mm (inches)
|
46
(1.81) |
18
(0.71) |
23
(0.91) |
58
(2.28) |
278
(10.94) |
295
(11.61) |
226
(8.9) |
298
(11.73) |
260
(10.24) |
285
(11.22) |
240
(9.45) |
186
(7.32) |
2,213
(87.12) |
Avg. rainy days
|
3
|
1
|
1
|
3
|
9
|
17
|
14
|
12
|
10
|
11
|
8
|
4
|
93
|
248.0
|
259.9
|
279.0
|
246.0
|
223.2
|
201.0
|
226.3
|
210.8
|
201.0
|
235.6
|
225.0
|
220.1
|
2,775.9
| |
There are also several man-made fresh-water ponds resulting from excavations made during construction of the airfield and road on the western half of the atoll rim. These fill from rainfall and from extending into the Ghyben-Herzberg lenses found on this island.
Climate
Precipitation: All precaution falls as rain, characterised by air-mass type showers. Annual rainfall averages 2213 mm, with the heaviest precipitation from May to December. February is the driest month with 18 mm of rain, and August the wettest month, averaging 298 mm of rain.
Temperatures: The surrounding sea surface temperature is the primary climatic control and temperatures are generally uniform throughout the year, with an average maximum of 30 °C (86 °F) by day during March and April, and 29 °C (84 °F) in July through September. Diurnal variation is approximately 3–4 °C (5.4–7.2 °F), falling to the low 27 °C (82 °F) by night. Humidity is high throughout the year. The almost constant breeze keeps conditions reasonably comfortable.
Winds: From December through March, winds are generally westerly at approximately 6 knots (11 km/h). During April and May winds are light and variable, ultimately backing to an east-southeasterly direction. From June through September the influence of the Southeast trades is felt, with speeds of 10-15 knots. During October and November winds again go through a period of light and variable conditions veering to a westerly direction with the onset of summer in the Southern Hemisphere.
Thunderstorms: Activity is generally noticed during the afternoon and evenings during the summer months (December through March) and when the Intertropical Convergence Zones is in the vicinity of the island.
Diego Garcia is at minimum risk from tropical cyclones due to its proximity to the equator where the coriolis parameter required to organize circulation of the upper atmosphere is minimal. Low-intensity storms have hit the island, including in 1901, which blew over 1,500 coconut trees, on September 16, 1944 which caused the wreck of a Royal Air Force PBY Catalina, September 1990 which demolished the tent city then being constructed for United States Air Force bomber crews during Operation Desert Storm, and on July 22, 2007, when winds exceeded 60 knots (110 km/h) and over 250 millimetres (9.8 in) of rain fell in 24 hours.
The island was somewhat affected by the tsunami caused by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake. Service personnel on the western arm of the island reported only a minor increase in wave activity. The island was protected to a large degree by its favourable ocean topography. About 80 km (50 mi) east of the atoll lies the 650 km (400-mile) long Chagos Trench, an underwater canyon plunging more than 4,900 m (16,000 ft). The depth of the trench and its grade to the atoll's slope and shelf shore makes it more difficult for substantial tsunami waves to build before passing the atoll from the east. In addition, near shore coral reefs and an algal platform may have dissipated much of the waves' impact. A biological survey conducted in early 2005 indicated erosional effects of the tsunami wave on Diego Garcia and other islands of the Chagos Archipelago. One 200-to-300-metre (220 to 330 yards) stretch of shoreline was found to have been breached by the tsunami wave, representing approximately 10 percent of the eastern arm. A biological survey by the Chagos Conservation Trust reported that the resulting inundation additionally washed away shoreline shrubs and small to medium-size coconut palms.


Vegetation
The first botanical observations of the island were made by Hume in 1883, when the coconut plantations had been in operation for a full century. Subsequent studies and collections during the plantation era were made in 1885, 1905, 1939, and 1967. Thus, very little of the nature of the pre-contact vegetation is known.
The 1967 survey, published by The Smithsonian is used as the most authoritative baseline for more recent research. These studies indicate the vegetation of the island may be changing rapidly. For example, J. M. W. Topp collected data annually between 1993 and 2003 and found that on the average three new plant species arrived each year, mainly on Diego Garcia. His research added fully a third more species to Stoddart. Topp and Martin Hamilton of Kew Gardens compiled the most recent checklist of vegetation in 2009, which can be found at this footnote.
In 1967, Stoddart described the land area of Diego Garcia as having a littoral hedge of Scaevola taccada, while inland, Cococ nucifera (Coconut) was the most dominant tree, covering most of the island. The substory was either managed and park-like, with understory less than 0.5 metres in height, or consisted of what he called "Cocos Bon-Dieu" – an intermediate story of juvenile trees and a luxuriant ground layer of self-sown seedlings – causing those areas to be relatively impenetrable.
There are also areas of remnant tropical hardwood forest at the sites of the plantation-era villages, as well as Casuarina equisetifolia (Iron Wood Pines) woodlands.
In 1997, the United States Navy contracted a vegetation survey that identified about 280 species of terrestrial vascular plants on Diego Garcia. None of these was endemic, and another survey in 2005 identified just 36 species as "native", meaning arriving without the assistance of humans, and found elsewhere in the world. No terrestrial plant species are of any conservation-related concern at present.
Of the 36 native vascular plants on Diego Garcia, there are 12 trees, five shrubs, seven dicotyledonherbs, three grasses, four vines, and five ferns.




.
.




.
Wildlife
All the terrestrial and aquatic fauna of Diego Garcia are protected, with the exception of certain game fish, rats and cats; hefty fines are levied against violators.
US Military Activities
During the Cold War era, the United States was keen to establish a military base in the Indian Ocean to counter Soviet influence in the region and protect the sea-lanes for oil transportation from the Middle East. The United States saw the island as a strategically important one. The value has been proven many times, with the island providing a "fixed aircraft carrier" for the United States during the Iranian Revolution, Iraqi Invasion of Kuwait, Operation Enduring Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom.
The United States military facilities on Diego Garcia have been known informally as Camp Justice and, after renaming in July 2006, as Camp Thunder Cove. Formally, the base is known as Naval Support Facility Diego Garcia (the U.S. activity) or Permanent Joint Operating Base (PJOB) Diego Garcia (the UK's term).

United States military activities in Diego Garcia have caused friction between India and the United States in the past. Various political parties in India repeatedly called for the military base to be dismantled, as they saw the United States naval presence in Diego Garcia as a hindrance to peace in the Indian Ocean. In recent years, relations between India and the United States have improved dramatically. Diego Garcia was the site of several naval exercises between the United States and Indian navies held between 2001 and 2004.
Naval Support Facility Diego Garcia
The Naval Support Facility Diego Garcia provides Base Operating Services to tenant commands located on the island. The command's mission is "To provide logistic support to operational forces forward deployed to the Indian Ocean and Persian Gulf AORs in support of national policy objectives.
As of January 2012, the facility supported the following tenant commands:
- Maritime Pre-Positioning Ships Squadron TWO
- Branch Health Clinic
- Naval Computer And Telecommunications Station Far East Detachment Diego Garcia
- Naval Mobile Construction Battalion Detachment
- Naval Media Center Detachment Diego Garcia
- Military Sealift Command Office Diego Garcia
- Mission Support Facility
- Fleet Logistics Center Diego Garcia
- NAVFAC FE
- 36 MSG Pacific Air Force
- Det 1, 75th AMOG (AMC)
- AFSPC Det 2, 22nd Space Operations Squadron (ARTS & GPS)
- AFSPC Det 2, 18th Space Surveillance Sqn (GEODSS)
- Additionally, the USS Emory S. Land (AS-39) is forward deployed to Diego Garcia.

Satellite and communication facilities
Air Force Satellite Control Network Station
The United States Air Force operates a remote tracking station on Diego Garcia. Its call sign is REEF. This facility became more vital after the closure of the Indian Ocean Station in 1996.
GEODSS Station
The United States Air Force Operates a station of the Ground-based Electro-optical Deep Space Surveillance system on the southern end of the atoll. 7.41173°S 72.45222°E

Global Positioning System Monitoring Station
Diego Garcia is one of the five control bases for the GPS, operated by the United States military. The United States Air Force also has monitoring stations in Hawaii, Kwajalein, Ascencion Island and Colorado Springs. The stations synchronise and update the atomic clocks on the 24 orbiting satellites that emit the signals used by GPS receivers.7.26654999°S 72.36312094°E.
HF Global Station
The United States Air Force operates a High Frequency Global Communications System transceiver site located on the south end of the atoll near the GEODSS station. The transceiver is operated remotely from Joint Base Andrews and locally maintained by NCTS FE personnel.
Naval Computer and Telecommunications Station Far East Detachment Diego Garcia
Naval Computer and Telecommunications Station Far East Detachment Diego Garcia operates a detachment in Diego Garcia. This detachment provides base telephone communications, provides base network services (Local Network Services Center), pier connectivity services, an AN/GSC-39C SHF satellite terminal, operates the Hydroacoustic Data Acquisition System, and performs on-site maintenance for the remotely operated Air Force HF-GCS terminal.
Naval Security Group Detachment Diego Garcia
Naval Security Group (NSG) detachment Diego Garcia was disestablished on September 30, 2005. Remaining essential operations were transferred to a contractor. The large AN/AX-16 High Frequency Radio direction finding Circulary Disposed Antenna Array has been demolished, but the four satellite antenna radomes around the site remain as of 2010.
ETOPS Emergency Landing Site
Diego Garcia may be identified as an ETOPS(Extended Range Twin Engine Operations) emergency landing site (en route alternate) for flight planning purposes of commercial airliners. This allows twin-engine commercial aircraft (such as the Airbus 330, Boeing 767 or 777) to make theoretical nonstop flights between city pairs such as Perth and Dubai and Dubai (9,013.61 km or 5,600.80 mi), Hong Kong and Johannesburg (10,658 km or 6,623 mi) or Singapore and Sao Paulo (15,985.41 km or 9,932.87 mi), all while maintaining a suitable diversion airport within 180 minutes' flying time with one engine inoperable.
Space Shuttle
The island was one of 33 emergency landing sites worldwide for the NASA Space Shuttle. None of these facilities were ever used throughout the life of the shuttle program.
Cargo Service
From 2004 to 2009, MV Baffin Strait, transited between Sinagpore and Diego Garcia once a month.
All consumable food and equipment is brought to Diego Garcia by sea or air, and all non-biodegradable waste is shipped off the island as well. From 1971 to 1973, United States Navy LSTs provided this service. Beginning in 1973, civilian ships were contracted to provide these services. From 2004 to 2009, the U.S.-flagged container ship MV Baffin Strait, often referred to as the "DGAR shuttle," delivered 250 containers every month from Singapore to Diego Garcia. The ship delivered more than 200,000 tons of cargo to the island each year. On the return trip to Singapore, it carried recyclable metals.
In 2004, Trans Atlantic Lines outbid Sealift Incorporated for the transport contract between Singapore and Diego Garcia. The route had previously been serviced by Sealift Inc.'s MV Sagamore, manned by members of American Maritime Officers and Seafarers’ International Union. TransAtlantic Lines reportedly won the contract by approximately 10 percent, representing a price difference of about US$2.7 million. The Baffin Straits charter ran from January 10, 2005, to September 30, 2008, at a daily rate of US$12,550.





Reference: www.wikipedia.com
The World's 18 Strangest Military Bases
THE WORLD'S HODGEPODGE OF MILITARY BASES RUN THE GAMUT FROM HAZARDOUS MOUNTAINTOP FORTS TO SEEMINGLY IMPENETRABLE UNDERGROUND BUNKERS. THEN THERE ARE BASES ON REMOTE ISLANDS TRACKING OBJECTS IN DEEP SPACE AND HIGH-TECH LABORATORIES PROBING THE MOST LETHAL MICROBES IN EXISTENCE. THE DESIGN OF A BASE NEEDS TO ADDRESS THE IMMEDIATE NEEDS OF A MILITARY WHILE STILL BEING VERSATILE ENOUGH TO REMAIN USEFUL AS THREATS AND TECHNOLOGY EVOLVE. WE TRACKED DOWN SOME OF THE MOST INTERESTING ACTIVE MILITARY FACILITIES AND SPOKE WITH BRAD SCHULZ, VICE PRESIDENT OF FEDERAL ARCHITECTURE AT HNTB, ABOUT WHY THEY'RE NOTABLE.
Navy Support Facility Diego Garcia
Diego Garcia BIOT, Chagos Archipelago:
Background: This joint U.S. and U.K. operation is situated on a tiny atoll about 1000 miles from India and tasked with providing logistical support to forces in Afghanistan and Iraq.
How It's Unique: "There's a certain amount of logistical difficulty" with ultra-remote facilities like Diego Garcia, Schulz says, and shipping materials can be costly. Diego Garcia's remoteness, though, allows it to be a key hub for tracking satellites, and it is one of five monitoring stations for GPS. Additionally, the island is one of only a handful of locations equipped with a Ground-based Electro-Optical Deep Space Surveillance system for tracking objects in deep space. As an atoll, the land itself is rather oddly shaped, too. From end to end, Diego Garcia is 34 miles long, but its total area is only 11 square miles.
Background: This joint U.S. and U.K. operation is situated on a tiny atoll about 1000 miles from India and tasked with providing logistical support to forces in Afghanistan and Iraq.
How It's Unique: "There's a certain amount of logistical difficulty" with ultra-remote facilities like Diego Garcia, Schulz says, and shipping materials can be costly. Diego Garcia's remoteness, though, allows it to be a key hub for tracking satellites, and it is one of five monitoring stations for GPS. Additionally, the island is one of only a handful of locations equipped with a Ground-based Electro-Optical Deep Space Surveillance system for tracking objects in deep space. As an atoll, the land itself is rather oddly shaped, too. From end to end, Diego Garcia is 34 miles long, but its total area is only 11 square miles.
No comments:
Post a Comment